Analytics, Baltic States – CIS, EU – Baltic States, Forum, Latvia, Markets and Companies, Statistics
International Internet Magazine. Baltic States news & analytics
Monday, 02.02.2026, 06:17
Facts and figures about the Eastern Partners of the European Union
 Print version
Print version
On the occasion of the 4th Eastern Partnership summit, which will take place on 21 and 22 May in Riga, Eurostat, the statistical office of the European Union, issues some selected data2 on demography, economy and trade in goods for the EU, its Member States and the Eastern Partners. A selection of infographics is also available on the Eurostat website.
A
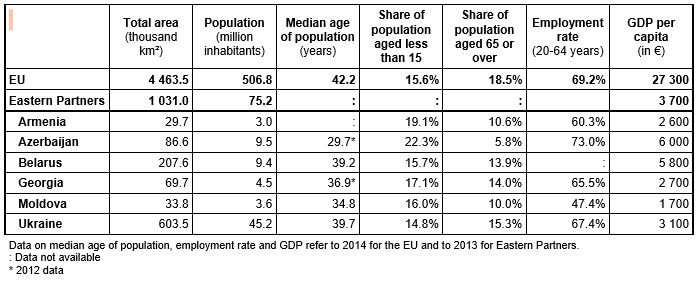
75-million-strong partnership All together, the Eastern partners’ surface area
is just over 1 million km² (a quarter of that of the EU) and their population
amounted in 2014 to 75.2 million (compared with 506.8 million in the EU).
Ukraine is the largest Eastern Partner, with an area (603.5 thousand km²)
approximately that of France (632.8 thousand km²), the largest EU Member State,
and a population roughly equivalent to that of Spain, standing at just over 45
million. In each Eastern partner country, the population was on average younger
than in the EU, with a median age ranging from 29.7 years in Azerbaijan to 39.7
years in Ukraine, compared with 42.2 years in the EU.
Standing on average at €3 700, the GDP per capita of the Eastern partners represented 14% of that of the EU, the lowest being recorded in Moldova (€1 700) and the highest in Azerbaijan (€6 000, nearly that of Bulgaria). Across the Eastern Partner countries, the employment rate of the population aged 20 to 64 varied considerably but was everywhere lower than in the EU (69.2%), except in Azerbaijan where it was 73.0%.
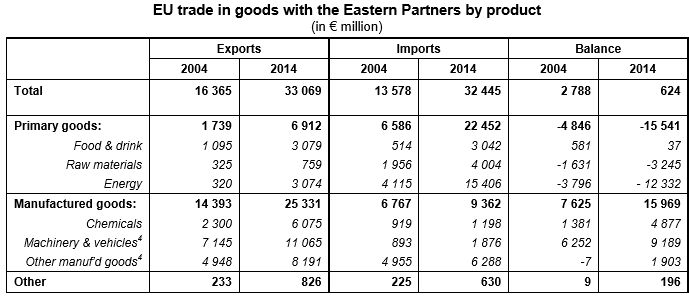
EU trade in goods with Eastern Partners almost in balance in 2014 After a significant decrease in 2009 following the financial crisis, the value of EU exports of goods to the Eastern Partners recovered until 2013 to reach a peak of €41.3 bn and then fell again in 2014 to €33.1 bn. Imports also recovered after 2009 to hit €36.7 bn in 2011, and then decreased continuously to €32.4 bn in 2014. As a result, EU trade with the Eastern Partners was almost in balance in 2014 (+€0.6 bn). In 2014, the six Eastern Partners accounted together for nearly 2% of total extra-EU trade in goods, almost equivalent to Saudi Arabia, the EU’s 11th most important trading partner.
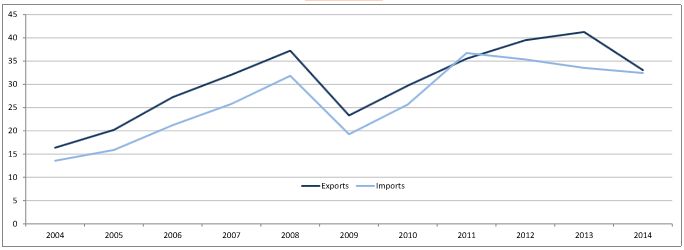 |
| Evolution of EU exports and imports of goods with the Eastern Partners, 2004-2014 (in € billions) |
EU exports to Eastern Partners dominated by manufactured goods, imports by primary goods Among the Eastern partner countries, Ukraine (€17.1 bn or 52% of total EU exports to the Eastern Partners) was the leading destination for EU exports in 2014. The leading source of EU imports from the Eastern Partners was also Ukraine (€13.8 bn or 42% of total EU imports from the Eastern Partners), closely followed by Azerbaijan (€13.2 bn or 41%). It should be noted that Azerbaijan accounted for 84% of EU energy imports from the Eastern Partnership countries, leading to a trade deficit for the EU with this country (-€9.7 bn). In contrast, the largest EU surpluses with the Eastern Partners in 2014 were recorded with Belarus (+€4.0 bn) and Ukraine (+€3.4 bn).
EU exports of goods to the Eastern partner countries are led by manufactured goods, which accounted for more than three-quarters (77%) of total exports. Conversely, EU imports from the Eastern Partners were dominated by primary goods, representing around 70% of total EU imports from these countries.
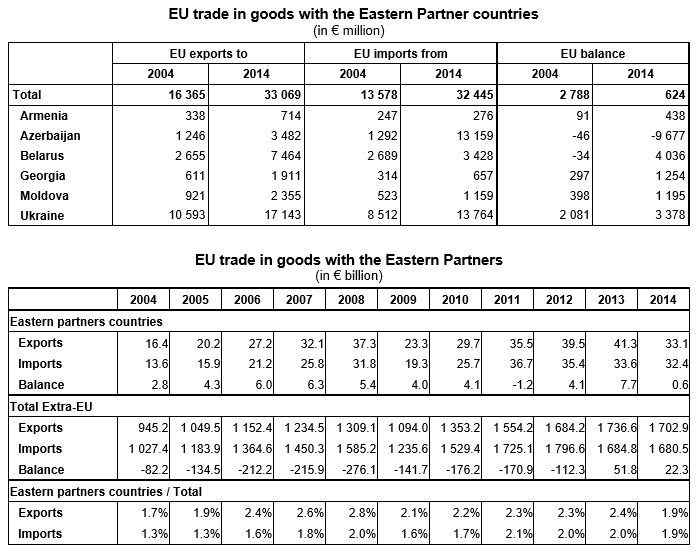
Germany, Italy and Poland: largest EU traders with the Eastern Partners Among the EU Member States, Germany (€7.0 bn or 21% of EU exports of goods to the Eastern Partners) and Poland (€5.2 bn or 16%) were by far the largest exporters to the Eastern partner countries in 2014, followed by Italy (€2.8 bn or 8%), Lithuania (€2.2 bn or 7%) and Hungary (€2.1 bn or 6%). Compared with 2004, exports to the Eastern Partners increased in 2014 in all EU Member States, except Sweden. At EU level, the value of exports of goods to the Eastern Partners has doubled over the last ten years.
Italy
(€8.2 bn or 25% of EU imports of goods from the Eastern Partners) was the
largest importer from the Eastern partner countries in 2014, well ahead of Germany
(€4.5 bn or 14%), Poland (€2.4 bn or 8%), the Czech Republic (€2.3 bn or 7%),
France and Spain (both around €2.0 bn or 6%). Compared with 2004, EU imports of
goods from the Eastern Partners increased by around 140% in 2014.
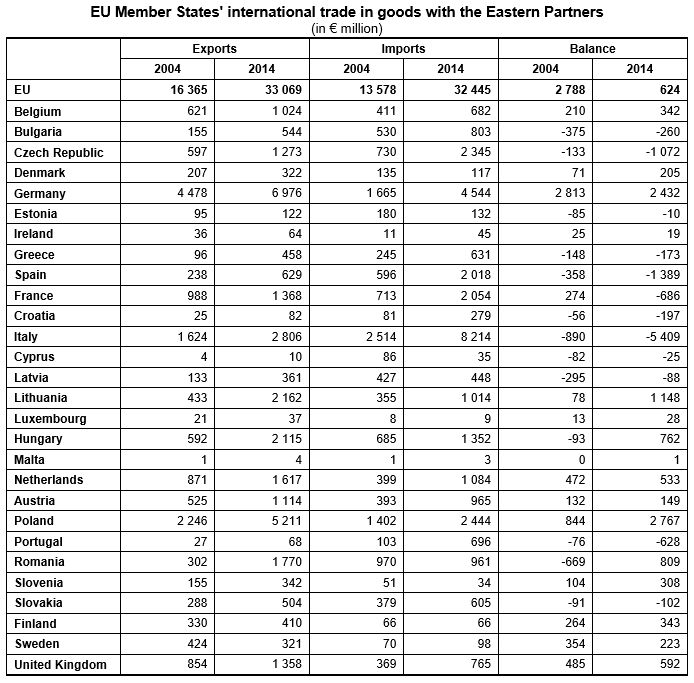
Sixteen EU Member States recorded a surplus in trade with the Eastern partner countries in 2014, with Poland (+€2.8 bn) and Germany (+€2.4 bn) continuing to have the largest surpluses. The largest deficit in 2014 was observed by far in Italy (-€5.4 bn), followed by Spain (-€1.4 bn) and the Czech Republic (-€1.1 bn).
More information on the Eastern Partnership can be found at:
1. http://eeas.europa.eu/eastern/index_en.htm
2. Further data on the European Neighbourhood Policy countries are available in
the dedicated section of the Eurostat website:
http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/european-neighbourhood-policy/enp-east
as well
as in a Statistics Explained article:
http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/European_Neighbourhood_Policy_countries__statistical_overview
3. Facts and figures on EU international trade in goods with Eastern partners are presented in the “Themes in the spotlight” section of the Eurostat website: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/news/themes-in-the-spotlight 4. Machinery and vehicles includes power generating and industrial machinery, computers, electric and electronic parts and equipment, road vehicles and parts, ships, airplanes and railway equipment. Other manufactured goods includes articles made of leather, rubber and wood, paper, textiles, metals, building fixtures and fittings, furniture, clothes, shoes and accessories, scientific instruments, clocks, watches and cameras.








 «The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!
«The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!

