Analytics, EU – Baltic States, Financial Services, Wages
International Internet Magazine. Baltic States news & analytics
Tuesday, 16.04.2024, 06:24
European Wage Inflation
BC, Riga, 27.03.2019. Print version
Print version
 Print version
Print versionWith the drama of the U.K. parliament unfolding and changing by the hour, this
week, DBRS has chosen a chart that highlights a positive development — at least
for wage earners.
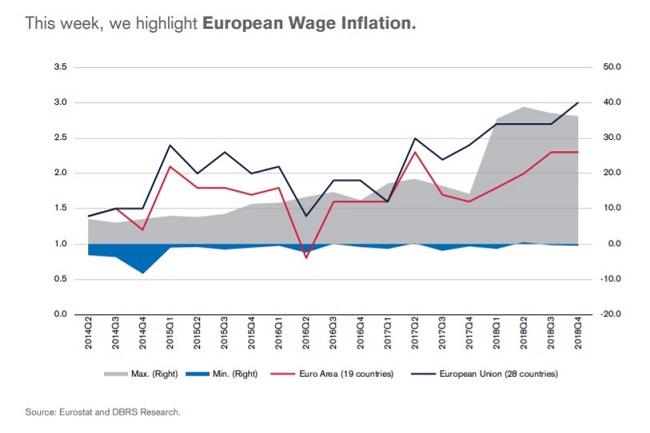
An increase in wages should result in an increase in inflation, which will put
pressure on the ECB to pull back on its quantitative easing. However, while wage increases signal potential inflation, there are plenty of negative headwinds
currently on the horizon, as a number of European countries are showing signs of
slowing growth.
Additionally, there is wide variation in the levels of wage inflation per country.
Some countries, such as Malta (-0.4% wage decrease), Spain (1.2% wage increase),
Italy (1.7%) and France (1.9%), have wage growth below 2.0%. On the other hand,
several countries have regularly high growth over the year, which continued in
the Q4 2018, including Romania (13.1%), Hungary (10.4%) and Latvia (10.2%).
Other notable countries are the U.K. (3.4%), Germany (2.4%) and Netherlands
(2.3%). These statistics represent year-over-year quarterly changes in wage and
salary costs.








 «The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!
«The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!

