Analytics, Baltic States – CIS, Direct Speech, Education and Science, EU – Baltic States, Latvia, Uzbekistan
International Internet Magazine. Baltic States news & analytics
Saturday, 20.04.2024, 10:12
The implementation of the social policy for 25 years of Independence of the Republic of Uzbekistan
 Print version
Print version |
|---|
The 25th anniversary of the Independence of the Republic of Uzbekistan which took place in 2016 was marred by a sad event – the death of the first president of the Republic of Uzbekistan – Islam Karimov. The whole nation mourned, in other words, the whole civilized world mourned - both in the East and in the West, news agencies loudly announced about the immeasurable contribution of Islam Karimov not only to the economy of his state, but also to the world economy as a whole. Having recovered from the loss, analysts turn to the phenomenon of building an independent state which in such short period has achieved good results.
Really common in the programs of development of the mentioned states and Uzbekistan – it is the restructuring of the agricultural sector into the industrial and development of industries. However, the above-mentioned states, the first president of Uzbekistan I. Karimov, with the transition to a market economy and industrialization of the state, focused on the social program for the citizens of his country.
Here, within the frameworks of our research, the reference should be made to five key principles of the policy of the transition period formulated by the resident Islam Karimov and within the frameworks of our research to focus on the first principle: the economy must have a priority over policy, be its internal content. The policy is the reflection of the economy and should serve its further development. Economy and policy don’t function separately. They are inextricably connected with each other and make up the two sides of a single whole. In this interrelation the priority is given to the economy as the primary link of a unified system. This doesn’t mean a secondary policy. The economic policy is designed to strengthen the economy, to determine the strategy of its development. An ill-considered, unjustified, erroneous economic policy can have a disastrous impact on the economy, to doom to failure and to disrupt the ultimate goal. Economy and policy in unity and in full harmony should move towards the main social goal – raising the living standards of the population and its social security[1].
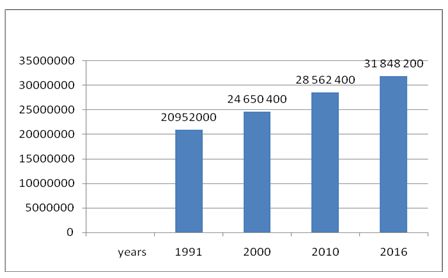
Not without reason this principle is set by the first president – the economy should dominate over policy and the main goal is stated – raising the living standards of the population and its security, have determined all the subsequent programs for the next 25 years, but it is thought for many decades. With what resource did the country become independent? The main indicator for the state – it is the size of its population, in fact, on what resource the social program should be calculated. (Figure 1).
Figure 1. The dynamics of the population of the Republic of Uzbekistan in the period from 1991 to 2016 (Developed by the author).
Source: The International Monetary Fund

Figure 2. The gross domestic product per capita in Uzbekistan, USD dollar. Developed by the author. Source: World Bank [4].
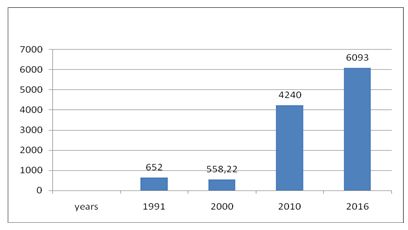
As we see from the represented data in Figure 2, if in 1992 the income per capita in Uzbekistan was 652.82 USD dollars, then, in 2016 this indicator increased almost 10 times and made up - 6039 USD dollars according to the estimate of the IMF[5].
The construction of the new state required not only political stability in the external market, but also the social stability and social security of the population of Uzbekistan. The implementation of social programs of the country under the leadership of the first President Islam Karimov and Shavkat Mirziyoyev elected in 2016 can be estimated through the indicator of the unemployment rate in the country (Figure 3).
Figure 3. The level of unemployed people in the Republic of Uzbekistan in the period from 1992 to 2016, %, Figure of the author. Source: International Monetary Fund
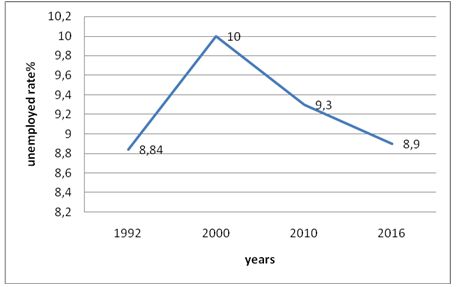
As the graph shows in Figure 1, if the population level for the examined period has increased by 52 %, then, the level of unemployment is at a fairly stable level for the country and ranges from 8.84% to 10% per year [6]. In the EU countries unemployment makes it difficult to solve the social problems, as the maximum level of unemployed people in 2016 in the EU countries, in Spain was – 19.6 %, (with the population in 2016 - 46 440 099 people), in Greece – 23.6% (the number of population in 2016. – 10 783 748 people.), in general, in EU countries -28th unemployment rate in 2000 was 8.9%, in 2010 -9.6%, but in 2016 – 8.6% [7].
As we can see, Uzbekistan, despite the global economic crisis has maintained a fairly stable position in the labour market in its country, providing citizens with the social stability [8].
Figure 4. The lifetime in the Republic of Uzbekistan in the period from 1991 to 2016, developed by the author. Source: International Monetary Fund
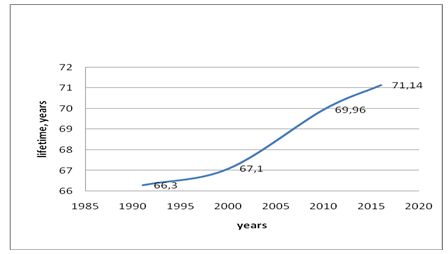
The following indicator for the assessment of the implementation of the social program and improving the people’s wellbeing of Uzbekistan is the indicator of lifetime, which is included in almost all world ratings of assessment of the quality of life. The uniqueness of the implementation of social programs of Uzbekistan, related to the care of young people, the elderly, mother and child – all these activities allow solving problems holistically in one of the social groups. This is perhaps one of the peculiarities of the implementation of the social policy in Uzbekistan. There are no analogues in Europe and this is his own, individual approach in the implementation of social policy.
Thus, the country entered the construction of an independent state in 1991 with an average lifetime of 66 years and for 25 years on the average the residents of the country, as a result of carried out reforms in the country has increased the average lifetime by another 5 years, as in 2016 the average lifetime in the country was already 71 years [9].
The implementation of the social policy in the country with care for the needs of the population clearly demonstrates the mentioned economic indicators, but it should the main aspect that programs are implemented on the basis of intensive economic growth of the state and this is the inheritance of the implementation of the economic and social programs of the first president of the Republic of Uzbekistan of Islam Karimov within 25 years!
The growth of the gross domestic product of the country of the Republic of Uzbekistan, let’s represent in the graph (Figure 5).
Figure 5. The growth of GDP in the Republic of Uzbekistan in the period from 1991 to 2016, developed by the author. Source: World Bank
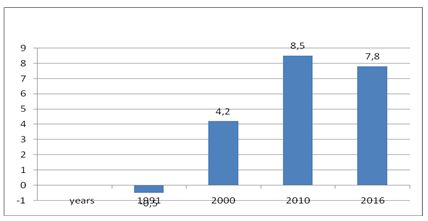
Thus, as we see from the graph, represented by the author, the construction of the independent Republic of Uzbekistan began with the fall of the GDP of the country in 1991 «– 0,5%»![10], however, in recent years the country shows an annual growth of GDP in 7-8%, that provides opportunities not only for construction of new industries, innovative industries, but also the social support is provides, as well as the social security of the residents of Uzbekistan.
Certainly, it is impossible to reflect the multifacetedness of issues on several graphs, their solutions and achievements over the past 25 years of the independent development of the Republic of Uzbekistan. However, we would like to reflect a small, but infinitely important part of the development of the country, not only with the help of graphs and figures, but also with the understanding of the contribution of the President Islam Karimov to the solution of the social issues. What is the phenomenon of the rapidly growing economy of Uzbekistan? Perhaps in the development of the market economy, with the active support of the state and the creation of a stable, socially protected economy in the country for the successful and all- round development of the quality of life of the population that reflects the indicators: the growing number of population, the growth of well-being and lifetime.
All the indicators mentioned by us demonstrate the correctness and timeliness of the priorities of the economic development adopted by the President Islam Karimov and we can confidently say that the experience of Uzbekistan will enter the world economy as “the Uzbek model of implementation of the economic policy”.
The list of references:
[1]. И.А. Каримов, Узбекистан по пути углубления экономических реформ. – Т.: Узбекистан,
1995. – 245 с
[2]. International
Monetary Fund, Republic of Uzbekistan: Recent Economic
Development, https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/1998/cr98116.pdf -available 12.09.2017.
[3]. Евростат: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/table.do?tab=table&init=1&language=en&pcode=tsdec450&plugin=1 available 12.09.2017
[4]. World bank: https://data.worldbank.org/country/uzbekistan available14.09.2017.
[5] Inna Stecenko, Anvar Irchaev. Implementation of the social policy of
the Republic of Uzbekistan, sсientific journal of ACTA STING (data base ERIH
PLUS). Czech Republic, Brno, 2016, № 4.
[6] International Monetary
Fund, Republic of Uzbekistan: Recent Economic Development,
https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/1998/cr98116.pdf available 15.09.2017.
[7] Евростат: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/tgm/table.do?tab=table&init=1&language=en&pcode=tsdec550&plugin= available 14.09.2017.
[8] Инна Стеценко, Анвар Ирчаев. Оценка роли домохозяйств в экономике
Республики Узбекистан. Transformācijas process tiesībās reģionālajā ekonomika un ekonomiskajā politikā: ekonomiski-politisko un tiesisko attiecību aktuālās problēmas” rakstu krājums. Rīga, 2015, с.62-67.
[9] International
Monetary Fund. https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/1998/cr98116.pdf available 15.09.2017
[10] Word Bank,
https://data.worldbank.org/country/uzbekistan, available 17.09.2017.








 «The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!
«The Baltic Course» Is Sold and Stays in Business!

